在说明int(*pointer)[6];中,标识符pointer()。A、说明不合法B、是一个指针数组名,每个元素是一个指向整型变量的指针C、是一个指针,它指向一个具有六个元素的一维数组D、是一个指向整型变量的指针
题目
在说明int(*pointer)[6];中,标识符pointer()。
- A、说明不合法
- B、是一个指针数组名,每个元素是一个指向整型变量的指针
- C、是一个指针,它指向一个具有六个元素的一维数组
- D、是一个指向整型变量的指针
相似问题和答案
第1题:
从供选择的答案中选出应填入英语文句中()的正确的答案。
Toolboxes and menus in many application programs were (A) for working with the mouse. The mouse controls a pointer on the screen. You move the pointer by (B) the mouse over a flat surface in the direction you want the pointer to move. If you run out of (C) to move the mouse, lift it up and put it down again. The pointer moves only when the mouse is (D) the flat surface. Moving the mouse pointer across the screen does not affect the document, the pointer simply (E) a location on the screen. When you press the mouse button, something happens at the location of the pointer.
A: ① assigned ② designed ③ desired ④ expressed
B: ① putting ② sliding ③ serving ④ taking
C: ① board ② place ③ room ④ table
D: ① getting ② going ③ teaching ④ touching
E: ① constructs ② indicates ③ instructs ④ processes
A: ② B: ② C: ③ D: ④ E: ②
第2题:
针对以下C语言程序,请按要求回答问题。
已知link. c源程序如下:
/*link. c程序对单向链表进行操作,首先建立一个单向链表,然后根据用户的选择可以对其进行插入结点、删除结点和链表反转操作*/
include<stdio. h>
include<stdlib. h>
typedef struct list_node * list_pointer; //定义链表指针
typedef struct list_node{ //定义链表结构
int data;
list_pointer link;
}list_node;
//用到的操作函数
list_pointer create(); //建立一个单向链表
void insert(list_pointer * p_ptr,list_pointer node); //在node后加入一个新的结点
void delete_node(list_pointer * p_ptr,list_pointer trail,list_pointer node);
//删除前一个结点是trail的当前结点node
void print(list_pointer * p_ptr); //打印链表结点中的值
list_pointer invert(list_pointer lead); //反转链表
int main()
{
list_pointer ptr=NULL;
list_pointer node,trail;
list_pointer * P=&ptr;
int choose,location,i;
printf("you should create a link first:\n");
//建立一个单向链表
prt=create(); //ptr指向链表的第一个结点
print(ptr);
//根据用户的不同选择进行相应的操作:
printf("input number 0,you can quit the program\n");
printf("input number 1,you can insert a new node to link\n"):
printf("input number 2,you can delete a node from the link\n");
printf("input number 3,you can invert the link\n"):
printf("please input you choice\n");
scanf("%d",&choose);
while(choose!=0){
switch(choose){
case 1:
i=1:
while(i<location){
node=node->link;
i++:
}
insert(p,node); //p为指向ptr的指针
print(ptr);
break;
case 2:
printf("you will delete a node from the link\n");
printf("please input the location of the node:\n");
scanf("%d",&location):
node=ptr;
if(location==1)
trail=NULL;
trail=ptr;
i=1:
while(i<location){
trail=trail->link:
i++:
}
node=trail->link;
delete_node(p,trail,node);
print(ptr);
break;
case 3:
printf("you will invert the link\n");
ptr=invert(ptr);
print(ptr);
break;
default;
break;
return -1;
}
printf("please input you choice\n");
scanf("%d". &choose):
}
return 0;
//根据用户的输入值建立一个新的单向链表:
list_pointer create()
{
int i,current,length;
list_pointer p1,p2,head;
printf("please input the node number of the link:\n");
scanf("%d". &length):
printf("the number of the link is:%d",length);
printf("please input the data for the link node:\n");
i=0;
p1=p2=(list_pointer)malloc(sizeof(list_node));
head=p1;
for(i=1;i<length;i++){
scanf("%d",&current);
p1->data=current;
p2->link=p1;
p2=p1;
p1=(list_pointer)malloc(sizeof(list_node));
}
p2->link=NULL;
return head;
}
画出主函数main的控制流程图。
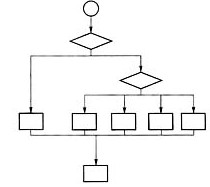
主函数的控制流程如下图所示。

第3题:
typedef int datatype; //结点的数据类型,假设为int
typedef struct NODE *pointer; //结点指针类型
struct NODE {
datatype data;
pointer lchild,rchild;
};
typedef pointer bitree; //根指针类型
答案: void moves(sqlist *L) { int i,j; datatype x; i=1;j=L->n; while(i< j) { while(L->data[i]< 0 && i< j) i++; while(L->data[j]>=0 && i< j) j--; if(i< j) { x=L->data[i];L->data[i]=L->data[j];L->data[j]=x; i++;j--; } } }
第4题:
单链表的删除操作
procedure delete(L:linklist; I:integer);
var p,q:pointer;
begin
p:=loc(L,I-1);
q:=p^.next;
p^.next:=q^.next;
dispose(q);
dec(L.len);
end;
第5题:
链表的定位函数
loc(I:integer):pointer; {寻找链表中的第I个结点的指针}
procedure loc(L:linklist; I:integer):pointer;
var p:pointer;
j:integer;
begin
p:=L.head; j:=0;
if (I>=1) and (I<=L.len) then
while j<I do begin p:=p^.next; inc(j); end;
loc:=p;
end;
第6题:
The ______ controls a pointer On the screen .When you move it,?the pointer moves too.
A.menu
B.icon
C.mouse
D.click
第7题:
You are attempting to parallel two AC generators and the synchroscope pointer is revolving in the slow direction. This indicates that the frequency of the incoming machine is
A.higher than the bus frequency
B.lower than the bus frequency
C.file same as file bus frequency but out of phase with it
D.the same as the bus frequency, and the circuit breaker may be closed at nay pointer position
第8题:
论述题 3 :针对以下 C 语言程序,请按要求回答问题( 18 分)
已知 link.c 源程序如下:
/*link.c 程序对单向链表进行操作 , 首先建立一个单向链表 , 然后根据用户的选择可以对其进行插入节点 、
删除节点和链表反转操作 */
#include
#include
typedef struct list_node *list_pointer; // 定义链表指针
typedef struct list_node{ // 定义链表结构
int data;
list_pointer link;
}list_node;
// 用到的操作函数:
list_pointer create(); // 建立一个单向链表
void insert(list_pointer *p_ptr, list_pointer node); // 在 node 后加入一个新的节点
void delete_node(list_pointer *p_ptr, list_pointer trail, list_pointer node);
// 删除前一个节点是 trail 的当前节点 node
void print(list_pointer ptr); // 打印链表节点中的值
list_pointer invert(list_pointer lead); // 反转链表
int main()
{
list_pointer ptr=NULL;
list_pointer node, trail;
list_pointer *p = &ptr;
int choose, location, i;
printf("you should create a link first:\n");
// 建立一个单向链表:
ptr=create(); /* ptr 指向链表的第一个节点 */
print(ptr);
// 根据用户的不同选择进行相应的操作:
printf("input number 0, you can quit the program\n");
printf("input number 1, you can insert a new node to link\n");
printf("input number 2, you can delete a node from the link\n");
printf("input number 3, you can invert the link\n");
printf("please input your choice\n");
scanf("%d", &choose);
while(choose!=0){
switch(choose){
case 1:
printf("you will insert a node to the link\n");
printf("please input the location of the node:\n");
scanf("%d", &location);
node = ptr;
i = 1;
while(i<location){
node = node->link;
i++;
}
insert(p, node); /* p 为指向 ptr 的指针 */
print(ptr);
break;
case 2:
printf("you will delete a node from the link\n");
printf("please input the location of the node:\n");
scanf("%d", &location);
node = ptr;
if(location ==1)
trail = NULL;
trail = ptr;
i = 1;
while(i<location){
trail = trail->link;
i++;
}
node = trail->link;
delete_node(p, trail, node);
print(ptr);
break;
case 3:
printf("you will invert the link\n");
ptr = invert(ptr);
print(ptr);
break;
default:
break;
return -1;
}
printf("please input your choice\n");
scanf("%d", &choose);
}
return 0;
}
// 根据用户的输入数值建立一个新的单向链表:
list_pointer create()
{
int i, current, length;
list_pointer p1, p2, head;
printf("please input the node number of the link:\n");
scanf("%d", &length);
printf("the number of the link is : %d\n", length);
printf("please input the data for the link node:\n");
i =0;
p1= p2= (list_pointer) malloc(sizeof(list_node));
head = p1;
for(i = 0; i
scanf("%d", ¤ t);
p1->data = current;
p2->link = p1;
p2 = p1;
p1 = (list_pointer) malloc(sizeof(list_node));
}
p2->link = NULL;
return head;
}
……
( 1 )画出主函数 main 的控制流程图。( 10 分)
( 2 ) 设计一组测试用例 , 尽量使 main 函数的语句覆盖率能达到 100% 。 如果认为该函数的语句覆盖率无法达到 100% ,需说明原因。( 8 分)

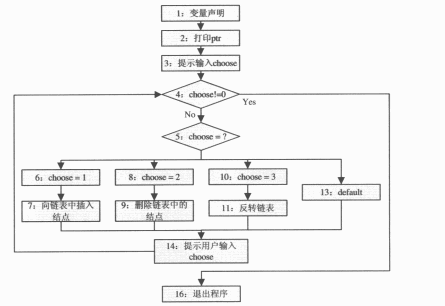



第9题:
单链表的插入操作
procedure insert(L:linklist; I:integer; x:datatype);
var p,q:pointer;
begin
p:=loc(L,I);
new(q);
q^.data:=x;
q^.next:=p^.next;
p^.next:=q;
inc(L.len);
end;
第10题:
Simplify the following Boolean expression
!((i ==12) || (j > 15))
struct Node {
int value;
Node* next;
};
1.1 Get the value of the Nth node from last node in the linked list.
PARAM HEAD: the first element in the linked list:
PARAM n: the number of the node counted reversely
RETURN: the value of the node, or -1 if not exists
int GetValue(Node* HEAD, int n)
{
}
1.2 Delete a node WITHOUT using the HEAD pointer.
PARAM p: A pointer pointed to a node in the middle of the linked list.
RETURN: void
void Delete(Node* p)
{
}
1.3 Insert a new node before p WITHOUT using the HEAD pointer
PARAM p: A pointer pointed to a node in the middle of the linked list.
PARAM value: new Node value
RETURN: void
void Insert(Node* p, int value)
{
}
Question 2:
Please write a String class with following features:
