有以下程序:include using namespace std;class Base{public:Base(){}virtual void w有以下程序: #include <iostream> using namespace std; class Base { public: Base(){} virtual void who() { cout<<"Base Class"<<end1; } ~Base(){} }; class Derivel : public Base { public: voi
题目
有以下程序: #include <iostream> using namespace std; class Base { public: Base(){} virtual void who() { cout<<"Base Class"<<end1; } ~Base(){} }; class Derivel : public Base { public: void who() { cout<<"Derivel Class"<<end1; } }; class Derive2 : public Base { public: void who () { cout<<"Derive2 Class"<<end1; } }; int main () { Base *p; Derivel obj1; Derive2 obj2; p=&obj1; p=&obj2; p->who ( ); return 0; } 执行程序后的输出结果是( )。
A.Base Class
B.Derivel Class
C.Derive2 Class
D.程序编译时出错
参考答案和解析
解析:本题考核虚函数的应用。本题中,先定义了一个基类Base,它含有一个虚成员函数who(),随后定义的类Derivel和Derive2都是基类Base的公有派生类。在主函数中定义了一个指向Base类的指针,它也被允许指向其派生类。在执行过程中,不断改变它所指向的对象,p->who就能调用不同的函数实现。这是因为使用了虚函数,因而进行动态联编。程序最后把指针p指向派生类Derive2的对象,由于函数who()在基类Base中是虚函数,所以系统调用Derive2中的who()函数,最后输出Derive2Class。
相似问题和答案
第1题:
【说明】
以下C++代码实现一个简单绘图工具,绘制不同形状以及不同颜色的图形。部分类及其关系如图6-1所示。
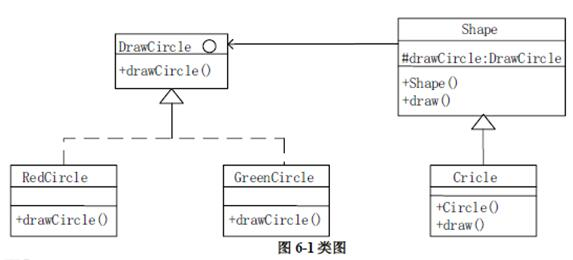
【C++代码】
#include?#include?using?namespace?std;class?DrawCircle?{??????//绘制圆形,抽象类? ? ? public: (1);//定义参数为?int?radius,?int?x,?inty? ?virtual~DrawCircle()?{?}};class?RedCircle:public?DrawCircle?{????//绘制红色圆形? ? ? ? public: void?drawCircle(intradius,?int?x,?int?y)?{cout?<?drawCircle?=?drawCircle;? }? ?virtual~shape()?{?}? public:? ?virtual?void?draw()?=?0;};class?Circle:public?Shape?{????//圆形? ? private:? ? ?int?x,y,radius;? ? public:? Circle(int?x,inty,int?radius,DrawCircle?*drawCircle)? (3)? {? this->x?=?x;? ?this->y?=?y;? ? this->radius?=?radius; }? ? ? public:? void?draw(){? drawCircle?-> (4); }};int?main(){Shape?*redCirclenew?Circle(100,100,10,????(5)????);//绘制红色圆形? Shape?*greenCircle=new?Circle(100,100,10, (6)??);//绘制绿色圆形redCircle >draw();? ?greenCircle?->draw();? ?return?0;}
(2)DrawCircle*drawCircle
(3)drawcircle
(4)drawCircle(radius,x,y)
(5)new RedCircle()
(6)new GreenCircle()【解析】
第一空是填接口里面的方法,在接口的实现里面找,可以发现应该填void drawCircle (int radius,int x,int y)。
第二空可以根据后面this drawCircle=drawCircle判断,这里应该有一个drawCircle属性,因此应该填)DrawCircle drawCircle。
第三空这里填drawcircle,用-> drawcircle来引用父类的成员。
第四空调用drawCircle(radius,x,y)方法。
第五、六空分别创建一个红色圆形对象和一个绿色圆形对象作为Circle里面的实参。
第2题:
若有以下程序: #include<iostream> using namespace Std; Class Base {public: Base() {x=0;} int x;}; class Derivedl:virtua1 public Base {public: Derived1() {x=10;}}; class Derived2:virtual1 public Base {public: Derived2()
A.20
B.30
C.10
D.0
解析: 本题考查虚基类的应用。虽然Derived1和Derived2都是由共同的基类x派生而来的,但由于引入了虚基类,使得它们分别对应基类的不同副本,这时数据成员x只存在一份拷贝,不论在类Derivedl中修改,还是在De- rived2中修改,都是直接对这惟一拷贝进行操作。本题程序执行语句“Derivedob“”时,就会先调用虚基类Base的构造函数,使得x=0,然后执行类Derived1的构造函数使得x=10,再执行类Derived2的构造函数,使得x=20。最后输出x的值为20。
第3题:
有以下程序#include <iostream>using namespace std:class Base{private: char c;public: Base(char n) :c(n) {} ~Base ( ) { cout<<c; }}; class Derived : public Base{private: char c;public: Derived(char n):Base (n+1),c(n) {} ~Derived() { cout<<c; }};int main(){ Derived obj('x'); return 0;} 执行后的输出结果是
A.xy
B.yx
C.x
D.y
解析:本题考核继承与派生中继承基类的数据成员与成员函数。在C++中,由于析构函数不能被继承,因此在执行派生类的析构函数时,基类的析构函数也将被调用。执行顺序是先执行派生类的析构函数,再执行基类的析构函数,其顺序与执行构造函数的顺序正好相反.在此题的程序中,在主函数main结束时,派生类Derived对象obj将被删除,所以就会调用对象的析构函数。先调用派生类的析构函数,输出x,然后调用基类的析构函数,输出y。
第4题:
有以下程序: #include <iostream> using namespace std; class BASE { private: char c; public: BASE(char n):c(n);{} virtual~BASE() { cout<<c; } }; class DERIVED:public BASE { char c; p
A.XY
B.YX
C.X
D.Y
解析:在C++中,由于析构函数不能被继承,因此在执行派生类的析构函数时,基类的析构函数也将被调用。执行顺序是先执行派生类的析构函数,再执行基类的析构函数,其顺序与执行构造函数的顺序正好相反。在此题的程序中,在主函数结束时,派生类DERIVED对象obj将被删除,所以就会调用对象的析构函数。先调用派生类的析构函数,输出X,然后调用基类的析构函数,输出Y。
第5题:
有以下程序: #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; class base { private: char baseName[10]; public: base ( ) { strcpy (baseName, "Base"); } virtual char *myName() {
A.DerivedBase
B.BaseBase
C.DerivedDerived
D.BaseDerived
解析:本题考核虚函数的应用。类Derived是从基类Base公有派生而来的。因此,Derived是基类Base的子类型。主函数中定义了一个基类对象bb和一个派生类对象dd。从程序中可看出,派生类Derived的对象dd交给了处理基类Base的对象的函数showPtr进行处理。由于在基类中函数myName被定义成虚函数,所以在函数showPtr中调用的myName函数为派生类的成员函数mySame,从而输出Derived。然后输出className,即基类名称Base。
第6题:
有如下程序: #include<iostream>#include<iosream> using namespace std; class BASE{ char c; public; BASE(char n):c(n){} virtual ~ BASE(){cout<<c;} }; class DERIVED; public BASE{ char c; public: DERIVED (char n): BASE (n+1)
A.XY
B.YX
C.X
D.Y
第7题:
下列程序的运行结果是______。
include<iostream.h>
class Base
{
public:
void f(int x){cout<<“Base:”<<x<<endl;}
);
class Derived:public Base
{
public:
void f(char*str){cout<<“Derived:”<<str<<endl;}
};
void main(void)
{
Base*pd=ne
Base:97。 解析: 本题主要考查两个知识点,一是基类指针可以指向派生类对象,并可以访问派生类的所有成员。二是在函数重载中进行隐式类型转换。如pd->f(‘a’);系统到底调用哪个重载函数呢?实参既不是派生类中的形参,也不是基类中f函数的形参类型。此时系统根据就近原则和从高优先级到低优先级的规则尝试隐式转换。单字符更接近整数,故调用的是基类的f函数。
第8题:
有以下程序:
include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Base
{
public:
Base()
{
K=0;
}
int x;
};
class Derivedl:virtual public Base
{
public:
Derivedl()
{
x=10;
}
};
class Derived2:virtua1 public Base
20。 解析: 本题中,虽然Derived1和Derived2由于引入了虚基类,使得它们分别对应基类的不同副本。这时数据成员x只存在一份拷贝,不论在类Derived1中修改,还是在类Derived2中修改,都是直接对这惟一拷贝进行操作。本题程序执行语句“Derived obi;”时,就会先调用虚基类Base的构造函数,使得x=0,然后执行类Derived1的构造函数使得x=10,再执行类Derived2的构造函数,使得x=20。最后输出x的值为20。
第9题:
有如下程序: #include<iostream.h> using namespace std; Class Base { public: Base(){cout<<“BB”;f();} void{(){cout<<“BF”;} }; class Derived:public Base { public: Derived(){cout<<“DD”;} void f(){cout<<“Df”;) }; int main
A.BBBfDD
B.BBDfDDDf
C.DD
D.DDBBBf
解析: 本趣考查的是类的继承和派生。派生类执行构造函数的一般次序为;首先调用基类构造函数,然后调用成员对象的构造函数,最后是派生类构造函数中的内容。题目中定义派生类对象d时,先调用基类Base的构造函数,输出BBBf,然后调用派生类Derived的构造函数,输出DD。
