(b) Explain the corporation tax and value added tax (VAT) implications of the following aspects of the proposedrestructuring of the Rapier Ltd group.(i) The immediate tax implications of the restructuring. (6 marks)
题目
(b) Explain the corporation tax and value added tax (VAT) implications of the following aspects of the proposed
restructuring of the Rapier Ltd group.
(i) The immediate tax implications of the restructuring. (6 marks)
相似问题和答案
第1题:
Assume that the corporation tax rates for the financial year 2004 apply throughout.
(b) Explain the corporation tax (CT) and value added tax (VAT) issues that Irroy should be aware of, if she
proceeds with her proposal for the Irish subsidiary, Green Limited. Your answer should clearly identify those
factors which will determine whether or not Green Limited is considered UK resident or Irish resident and
the tax implications of each alternative situation.
You need not repeat points that are common to each situation. (16 marks)
(b) There are several matters that Irroy will need to be aware of in relation to value added tax and corporation tax. These are set
out below.
Residence of subsidiary
Irroy will want to ensure that the subsidiary is treated as being resident in the Republic of Ireland. It will then pay corporation
tax on its profits at lower rates than in the UK. The country of incorporation usually claims taxing rights, but this is not by
itself sufficient. Irroy needs to be aware that a company can be treated as UK resident by virtue of the location of its central
management and control. This is usually defined as being where the board of directors meets to make strategic decisions. As
a result, Irroy needs to ensure that board meetings are conducted outside the UK.
If Green Limited is treated as being UK resident, it will be taxed in the UK on its worldwide income, including that arising in
the Republic of Ireland. However, as it will be conducting trading activities in the Republic of Ireland, Green Limited will also
be treated as being Irish resident as its activities in that country are likely to constitute a permanent establishment. Thus it
may also suffer tax in the Republic of Ireland as a consequence, although double tax relief will be available (see later).
A permanent establishment is broadly defined as a fixed place of business through which a business is wholly or partly carried
on. Examples of a permanent establishment include an office, factory or workshop, although certain activities (such as storage
or ancillary activities) can be excluded from the definition.
If Green Limited is treated as being an Irish resident company, any dividends paid to Aqua Limited will be taxed under
Schedule D Case V in the UK. Despite being non resident, Green Limited will still count as an associate of the existing UK
companies, and may affect the rates of tax paid by Aqua Limited and Aria Limited in the UK. However, as a non UK resident
company, Green Limited will not be able to claim losses from the UK companies by way of group relief.
Double tax relief
If Green Limited is treated as UK resident, corporation tax at UK rates will be payable on all profits earned. However, income
arising in the Republic of Ireland is likely to have been taxed in that country also by virtue of having a permanent
establishment located there. As the same profits have been taxed twice, double tax relief is available, either by reference to
the tax treaty between the UK and the Republic of Ireland, or on a unilateral basis, where the UK will give relief for the foreign
tax suffered.
If Green Limited is treated as an Irish resident company, it will pay tax in the Republic of Ireland, based on its worldwide
taxable profits. However, any repatriation of profits to the UK by dividend will be taxed on a receipts basis in the UK. Again,
double tax relief will be available as set out above.
Double tax relief is available against two types of tax. For payments made by Green Limited to Aqua Limited on which
withholding tax has been levied, credit will be given for the tax withheld. In addition, relief is available for the underlying tax
where a dividend is received from a foreign company in which Aqua Limited owns at least 10% of the voting power. The
underlying tax is the tax attributable to the relevant profits from which the dividend was paid.
Double tax relief is given at the lower rate of the UK tax and the foreign tax (withholding and underlying taxes) suffered.
Transfer pricing
Where groups have subsidiaries in other countries, they may be tempted to divert profits to subsidiaries which pay tax at lower
rates. This can be achieved by artificially changing the prices charged (known as the transfer price) between the group
companies. While they can do this commercially through common control, anti avoidance legislation seeks to correct this by
ensuring that for taxation purposes, profits on such intra-group transactions are calculated as if the transactions were carried
out on an arms length basis. Since 1 April 2004, this legislation can also be applied to transactions between UK group
companies.
If Green Limited is treated as a UK resident company, the group’s status as a small or medium sized enterprise means that
transfer pricing issues will not apply to transactions between Green Limited and the other UK group companies.
If Green Limited is an Irish resident company, transfer pricing issues will not apply to transactions between Green Ltd and the
UK resident companies because of the group’s status as a small or medium-sized enterprise and the existence of a double
tax treaty, based on the OECD model, between the UK and the Republic of Ireland.
Controlled foreign companies
Tax legislation exists to stop a UK company accumulating profits in a foreign subsidiary which is subject to a low tax rate.
Such a subsidiary is referred to as a controlled foreign company (CFC), and exists where:
(1) the company is resident outside the UK, and
(2) is controlled by a UK resident entity or persons, and
(3) pays a ‘lower level of tax’ in its country of residence.
A lower level of tax is taken to be less than 75% of the tax that would have been payable had the company been UK resident.
If Green Limited is an Irish resident company, it will be paying corporation tax at 12·5% so would appear to be caught by
the above rules and is therefore likely to be treated as a CFC.
Where a company is treated as a CFC, its profits are apportioned to UK resident companies entitled to at least 25% of its
profits. For Aqua Limited, which would own 100% of the shares in Green Limited, any profits made by Green Limited would
be apportioned to Aqua Limited as a deemed distribution. Aqua Limited would be required to self-assess this apportionment
on its tax return and pay UK tax on the deemed distribution (with credit being given for the Irish tax suffered).
There are some exemptions which if applicable the CFC legislation does not apply and no apportionments of profits will be
made. These include where chargeable profits of the CFC do not exceed £50,000 in an accounting period, or where the CFC
follows an acceptable distribution policy (distributing at least 90% of its chargeable profits within 18 months of the relevant
period).
Value added tax (VAT)
Green Limited will be making taxable supplies in the Republic of Ireland and thus (subject to exceeding the Irish registration
limit) liable to register for VAT there. If Green Limited is registered for VAT in the Republic of Ireland, then supplies of goods
made from the UK will be zero rated. VAT on the goods will be levied in the Republic of Ireland at a rate of 21%. Aqua Limited
will need to have proof of supply in order to apply the zero rate, and will have to issue an invoice showing Green Limited’s
Irish VAT registration number as well as its own. In the absence of such evidence/registration, Aqua Limited will have to treat
its transactions with Green Limited as domestic sales and levy VAT at the UK standard rate of 17·5%.
In addition to making its normal VAT returns, Aqua Limited will also be required to complete an EU Sales List (ESL) statement
each quarter. This provides details of the sales made to customers in the return period – in this case, Green Limited. Penalties
can be applied for inaccuracies or non-compliance.
第2题:
(c) Assuming that Joanne registers for value added tax (VAT) with effect from 1 April 2006:
(i) Calculate her income tax (IT) and capital gains tax (CGT) payable for the year of assessment 2005/06.
You are not required to calculate any national insurance liabilities in this sub-part. (6 marks)

第3题:
(c) the deferred tax implications (with suitable calculations) for the company which arise from the recognition
of a remuneration expense for the directors’ share options. (7 marks)

第4题:
(ii) Explain the income tax (IT), national insurance (NIC) and capital gains tax (CGT) implications arising on
the grant to and exercise by an employee of an option to buy shares in an unapproved share option
scheme and on the subsequent sale of these shares. State clearly how these would apply in Henry’s
case. (8 marks)
(ii) Exercising of share options
The share option is not part of an approved scheme, and will not therefore enjoy the benefits of such a scheme. There
are three events with tax consequences – grant, exercise and sale.
Grant. If shares or options over shares are sold or granted at less than market value, an income tax charge can arise on
the difference between the price paid and the market value. [Weight v Salmon]. In addition, if options can be exercised
more than 10 years after the date of the grant, an employment income charge can arise. This is based on the market
value at the date of grant less the grant and exercise priced.
In Henry’s case, the options were issued with an exercise price equal to the then market value, and cannot be exercised
more than 10 years from the grant. No income tax charge therefore arises on grant.
Exercise. On exercise, the individual pays the agreed amount in return for a number of shares in the company. The price
paid is compared with the open market value at that time, and if less, the difference is charged to income tax. National
insurance also applies, and the company has to pay Class 1 NIC. If the company and shareholder agree, the national
insurance can be passed onto the individual, and the liability becomes a deductible expense in calculating the income
tax charge.
In Henry’s case on exercise, the difference between market value (£14) and the price paid (£1) per share will be taxed
as income. Therefore, £130,000 (10,000 x (£14 – £1)) will be taxed as income. In addition, national insurance will
be chargeable on the company at 12·8% (£16,640) and on Henry at the rate of 1% (£1,300).
Sale. The base cost of the shares is taken to be the market value at the time of exercise. On the sale of the shares, any
gain or loss arising falls under the capital gains tax rules, and CGT will be payable on any gain. Business asset taper
relief will be available as the company is an unquoted trading company, but the relief will only run from the time that
the share options are exercised – i.e. from the time when the shares were acquired.
In Henry’s case, the sale of the shares will immediately follow the exercise of the option (6 days later). The sale proceeds
and the market value at the time of exercise are likely to be similar; thus little to no gain is likely to arise.
第5题:
(c) (i) Explain the capital gains tax (CGT) implications of a takeover where the consideration is in the form. of
shares (a ‘paper for paper’ transaction) stating any conditions that need to be satisfied. (4 marks)
(c) (i) Paper for paper rules
The proposed transaction broadly falls under the ‘paper for paper’ rules. Where this is the case, chargeable gains do not
arise. Instead, the new holding stands in the shoes (and inherits the base cost) of the original holding.
The company issuing the new shares must:
(i) end up with more than 25% of the ordinary share capital (or a majority of the voting power) of the old company,
OR
(ii) make a general offer to shareholders in the other company with a condition that, if satisfied, would give the
acquiring company control of the other company.
The exchange must be for bona fide commercial reasons and must not have as its main purpose (or one of its main
purposes) the avoidance of CGT or corporation tax. The acquiring company can obtain advance clearance from the
Inland Revenue that the conditions will be met.
If part of the offer consideration is in the form. of cash, a gain must be calculated using the part disposal rules. If the
cash received is not more than the higher of £3,000 or 5% of the total value on takeover, then the amount received in
cash can be deducted from the base cost of the securities under the small distribution rules.
第6题:
(b) Write a letter to Joanne setting out the value added tax (VAT) registration requirements and advising on
whether or not she should or could register for VAT and if registered if she could recover the VAT suffered on
the consultancy fees and computer purchased in October 2005. (7 marks)
(b) [Joanne’s address] [Firm’s address]
Dear Joanne 5 February 2006
I am writing to you in order to set out the value added tax (VAT) issues you face on registering your trade, together with some
other aspects of VAT that are relevant to you.
Registration
VAT registration is compulsory once taxable supplies exceed £58,000. This turnover figure is based on the value of your
cumulative taxable supplies in the previous 12 months. You have an obligation to inform. Customs within 30 days of the end
of the month in which the annual limit is exceeded. Registration will become effective on the first day of the following month.
VAT registration is also required if there are reasonable grounds for believing that the taxable supplies in the following 30 days
will exceed £58,000. In such cases, notification is required by the end of that 30 day period with registration being effective
from the start of that period.
Based on your estimates of taxable supplies, you will exceed the annual limit in October 2006 when your cumulative turnover
will be £62,000. You will therefore have to inform. Customs by the end of November. Your registration will be effective as of
1 December 2006.
You also have the option of voluntarily registering prior to then in which case you will normally become registered from the
date you applied. This is useful where your sales are to VAT registered customers for whom the extra VAT would not be a cost.
You would then be able to recover VAT on your attributable costs. However, you will have to comply with the VAT
administrative requirements.
Recovery of pre-registration VAT
It is possible to claim the recovery of VAT incurred prior to registering for VAT. There are some conditions, however. The costs
of the goods or services must have been incurred for the purpose of the business and there are time limits. You have three
years from the effective date of registration to recover the VAT on fixed assets (such as your computer) but only six months in
the case of purchased services (such as the consultancy fees).
As a result, I would recommend that you apply for voluntary registration as soon as possible, as registering after 1 April 2006
will mean that you will be unable to reclaim the VAT on your consultancy fees.
I hope the above information is useful to you.
Yours sincerely,
A. Consultant.
第7题:
(b) (i) Advise Alasdair of the tax implications and relative financial risks attached to the following property
investments:
(1) buy to let residential property;
(2) commercial property; and
(3) shares in a property investment company/unit trust. (9 marks)
(b) (i) Income tax:
Direct investment in residential or commercial property
The income will be taxed under Schedule A for both residential and commercial property investment. Expenses can be
offset against income under the normal trading rules. These will include interest charges incurred in borrowing funds to
acquire the properties. Schedule A losses are restricted to use against future Schedule A profits, with the earliest profits
being relieved first.
When acquiring commercial properties, it may be possible to claim capital allowances on the fixtures and plant held in
the building. In addition, industrial buildings allowances (IBA) may also be available if the property qualifies as an
industrial building.
Capital allowances are not normally available for fixtures and fittings included in a residential property. Instead, a wear
and tear allowance can be claimed if the property is furnished. This is equal to 10% of the rental income after any
tenants cost (for example, council tax) paid by the landlord.
Income tax is levied at the normal tax rates (10/22/40%) as appropriate.
Collective investment (shares in a property investment company/unit trust)
With collective investments, the investor either buys shares (in an investment company) or units (in an equity unit trust).
The income tax treatment of both is the same in that the investor receives dividends. These are taxed at 10% and 32·5%
respectively (for basic and higher rate taxpayers).
Investors are not able to claim income tax relief on either interest costs (of borrowing) or any other expenses.
Capital gains tax (CGT):
The normal rules apply for CGT purposes in all situations. Property investments do not normally qualify for business
rates of taper relief unless they are furnished holiday lets or in certain circumstances, commercial property. Investments
in unit trusts or property investment companies will never qualify for business taper rates.
It is possible to use an individual savings account (ISA) to make collective investments. If this is done, income and
capital gains will be exempt from tax.
Other taxes:
New commercial property is subject to value added tax (VAT) at the standard rate, but new residential property is subject
to VAT at the zero rate. If a commercial building is acquired second hand as an investment, VAT may be payable if a
previous owner has opted to tax the property. If this is the case, VAT at the standard rate will be payable on the purchase
price, and rental charges to tenants will also be subject to VAT, again at the standard rate.
The acquisition of shares is not subject ot VAT.
Stamp duty land tax (SDLT) will be payable broadly on the direct acquisition of any property. The rates vary from 0 to
4% depending on the value of the land and building and its nature (whether residential or non-residential). Stamp duty
is payable at a rate of 0·5% on the acquisition of shares.
Investment risks/benefits
Direct investment
Investing directly in property represents a long term investment, and unless this is the case, investment risks are high.
Substantial initial costs (such as SDLT, VAT and transactions costs) are incurred, and ongoing running costs (such as
letting agents’ fees and vacant periods) can be significant. The investments are illiquid, particularly commercial
properties which can take months to sell.
All types of properties are dependent on a cyclical market, and the values of property investments can vary significantly
as a result. However, residential property has (on a long term basis) proven to be a good hedge against inflation.
Collective investments
The nature of collective investments is that the investor’s risk is reduced by the investment being spread over a large
portfolio as opposed to one or a few properties. In addition, investors can take advantage of the higher levels of liquidity
afforded by such vehicles.
第8题:
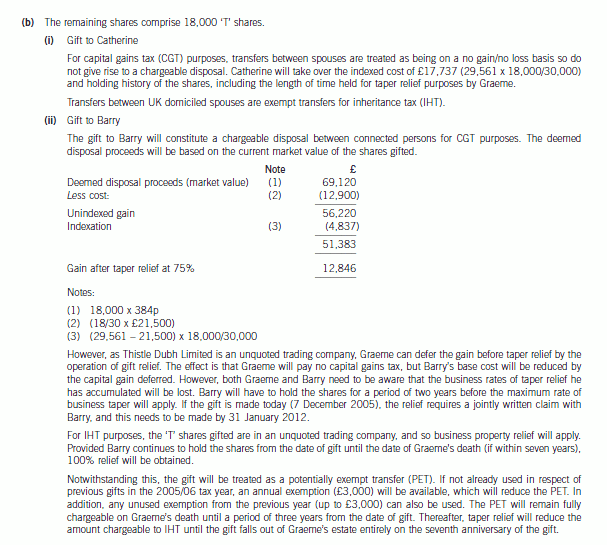
(b) Explain the capital gains tax (CGT) and inheritance tax (IHT) implications of Graeme gifting his remaining ‘T’
ordinary shares at their current value either:
(i) to his wife, Catherine; or
(ii) to his son, Barry.
Your answer should be supported by relevant calculations and clearly identify the availability and effect of
any reliefs (other than the CGT annual exemption) that might be used to reduce or defer any tax liabilities
arising. (9 marks)
第9题:
(b) Calculate the corporation tax (CT) liabilities for Alantech Ltd, Boron Ltd and Bubble Ltd for the year ending
31 December 2004 on the assumption that loss reliefs are taken as early as possible. (9 marks)
(b) Schedule D Case I calculation
The three companies form. a group for both group relief and capital gains purposes as all shareholdings pass the 75%
ownership test. The calculation of the corporation tax liabilities is as follows:

第10题:
(ii) Briefly outline the tax consequences for Henry if the types of protection identified in (i) were to be
provided for him by Happy Home Ltd compared to providing them for himself. You are not required to
discuss the corporation tax (CT) consequences for Happy Home Ltd. (4 marks)
(ii) Provision of protection: company or individual
If any of the policies are taken out and paid for by Henry personally, then there will be no tax relief on the premiums,
but neither will there normally be any tax payable on the proceeds or benefits received.
If Happy Home Ltd were to pay the premiums on a policy taken out by Henry, and of which he was the direct beneficiary,
then this will constitute a benefit, on the grounds that the company will have satisfied a personal liability of Henry’s.
Accordingly, income tax and Class 1A national insurance contributions will be payable on the benefit.
If, however, Happy Home Ltd were to decide to offer protection benefits to their employees on a group basis (and not
just to Henry), then it would be possible to avoid a charge under the benefits rules and/or obtain a lower rate of premium
under a collective policy. For example:
– A death in service benefit of up to four times remuneration can be provided as part of an approved pension scheme.
No benefit charge arises on Henry and any lump sum will be paid tax free. This could be considered a substitute
for a term assurance policy.
– If a group permanent health insurance policy were taken out, no benefit charge would arise on Henry, but any
benefits payable under the policy would be paid to Happy Home Ltd in the first instance. When subsequently paid
on to Henry, such payments would be treated as arising from his employment and subject to PAYE and national
insurance as for normal salary payments.
– If a group critical illness policy were taken out, again no benefit charge would arise on Henry, but in this case also,
any benefits received by Henry directly from Happy Home Ltd as a result of the payments under the policy would
be considered as derived from his employment and subject to income tax and national insurance. Such a charge
to tax and national insurance would however be avoided if these payments were made in terms of a trust.
